Stack and Queue Data Structures
My summary of stack and queue data structures
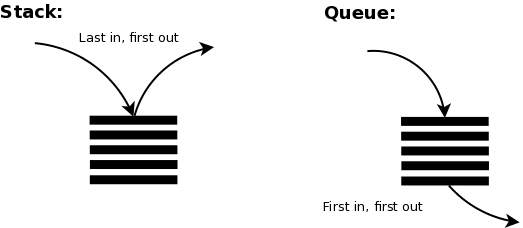
Stack and queue models are storage mechanisms built on memory, where data is temporarily stored, whose behavior is completely opposite to each other.
Last in first out (LIFO) in stack model, first in first out (FIFO) in queue model.
There are 3 basic operations required in stack and queue models. These are add, receive, reset/dump operations. In stack these are called the push, pop, reset; in the queue, these are called the add, get, reset operations respectively.
A queue can be implemented in 3 ways: sliding the array, cyclical array, and the linked list.
Queue
The cyclical array is always preferable over the sliding array method because it is better in terms of time complexity. That’s why I will not show the implementation of the sliding array method.
The linked list is preferable when we want dynamic allocation.
Queue linked list implementation
static NODE *first=NULL, *last=NULL;
int temp;Add
if(p=malloc(sizeof(NODE))==NULL){ puts("No empty space on memory"); return -1;
}
p->data=data;
p->next=NULL;
if(first==NULL){ first=p; last=p;
}
else{ last->next=p; last=p;
}
return 0;
Get
if(first==NULL){puts("Queue is empty");return -1;
}
p=First;
first=first->next;
if(first==NULL){last=NULL;}
temp=p->data;
free(p);
return temp;
Reset
while(first!=NULL){ p=first; first=p->next; free(p);
}
last=NULL;
return 0;
Stack implementation
Stack’s have a stack pointer that points to the empty slot. The stack can be implemented by an array or a linked list. Array implementation requires knowing the total amount of data from the beginning(static). The time complexity for push and pop operations on a stack is O(1) for both array and linked list implementations.
Array Stack
#define N 500 //Max number of elements
int Sarr[N]={0},sp=0; //stack array and stack pointerPush on array
if(sp>=N){ puts("Stack is full"); return -1;
}
else{ Sarr[sp]=data; sp++;
}
Pop on array
if(sp<=0){ puts("Stack is empty"); return -1;
}
else{ return Sarr[--sp];}
Reset on array
sp=0;Linked List Stack
static stack_node *sp=NULL; stack_node *node,node_data;Push on linked list
g=malloc(sizef(stack_node));
if(node==NULL) return -1;
node->data=data;
node->next=sp;
sp=node;Pop on linked list
if(sp==NULL){return -1;}
node=sp;
node_data.data=sp->data;
sp=sp.next;
free(node);
return node_data.data;Reset on linked list
sp=NULL;Please don’t forget to applaud if you like my post. Thank you.
Resource
[1]Çölkesen,2016,Algoritma Geliştirme ve Veri Yapıları,Papatya Bilim Üniversite Yayıncılığı,İstanbul.
[2]Kurt Anderson,(?),Stacks and Queues:
