Member-only story
Basic Java 8 Features
Main Java 8 features: Lambda expressions, Stream API, and Date Time API explained.
Lambda Expressions
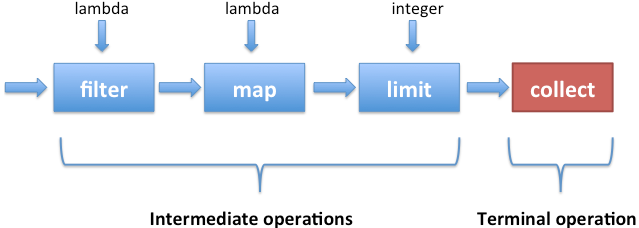
Lambda expressions are inline functions. They provide a straightforward and concise approach to use an expression to represent one method interface. It helps to iterate, filter, and extract data from a collection. [1]
We employ lambda expressions in order to give a functional interface with minimal coding.[2]
Syntax[2]:
For a single line of code:
(parameter1, parameter2) -> expressionOr for multiple lines of codes:
(parameter1, parameter2) -> {
code block
}Constraints
There are a few limitations for expression. They must return a value immediately and cannot contain variables, assignments, or phrases like if or for. A code block containing curly brackets can be used to do more sophisticated actions..[2]
//Without lambda, Drawable implementation using anonymous classDrawable d=new Drawable(){ public void draw(){
System.out.println(“Drawing “+width);
}});d.draw();
//with lambdaDrawable d2=()->{ System.out.println(“Drawing “+width);};d2.draw();
If there is only one statement, the return keyword may or may not be used. When a lambda expression contains several statements, you must use the return keyword.[1]
// Lambda expression without the return keyword.Addable ad1=(a,b)->(a+b);System.out.println(ad1.add(10,20));
// Lambda expression with return keyword.Addable ad2=(int a,int b)->{return (a+b);};//Example with collectionspublic static void…
